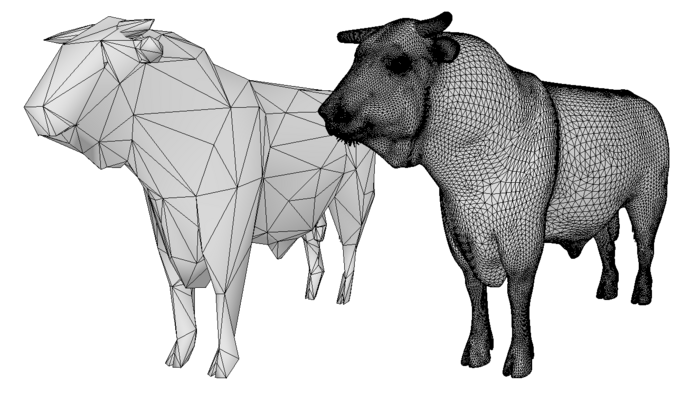
FROM CAD DATA TO LOW POLY MODELS FOR INTERACTIVE APPLICATIONS
UV unwrapping of data
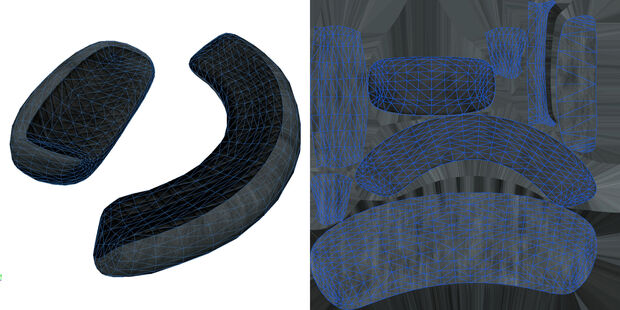

In the next step, known as "UV unwrapping," the finished models are virtually cut up and unfolded, similar to making a cube - only backwards. We can then apply various textures to the two-dimensional surface that this creates.
These textures contain, for example, information about color, roughness and reflective properties. Since ideally every spot on the model can be clearly assigned to a spot on the texture, we can thus depict individual details, whether material transitions, unevenness, symbols, stickers, rough edges, and so on.
Textures with subtleties

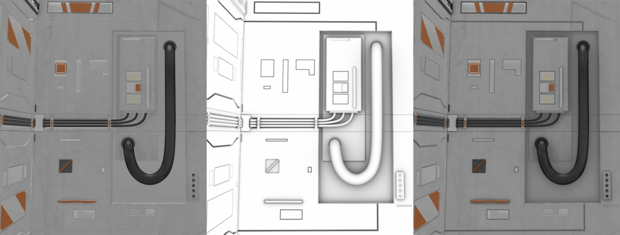
However, the textures are not limited to previous examples. They can even bring back the subtleties of the original, complex model. In doing so, they store the orientations of these surface details in colors. This allows the light to react to them without the need for additional polygons. In this way, we combine the performance of the simple model with the aesthetics of the complex model.
In addition, textures can contain a pre-calculated shading, the so-called Ambient Occlusion (AO). This increases contrast and makes it easier for the user to assess the shapes of the model shown faster and better.
If all these possibilities are exhausted and applied to a CAD model, then you get a performant and smoothly moving low poly model. Together with well done textures, it leads to an excellent user experience. No matter if in AR apps on mobile devices or in VR applications. A smoothly running application is fun and the resulting positive feeling is transferred to the product and the brand.
A few thoughts on the use of AR/VR in product development or in the business environment can be found in this BLOG.